- Americas
- Asia Pacific
- Europe
- Middle East and Africa

Manufacturing Outlook Report 2020
Examining the key concerns facing the manufacturing industry today and highlights the opportunities and challenges many people face in the day to day running of their business.
Despite some clear uncertainty over the impact of Brexit and wider global economic issues, there was a cautious mood of positivity for growth and prospects for 2020 and beyond from manufacturers responding to our survey, with the majority expecting their turnover to increase in the next 12 months.
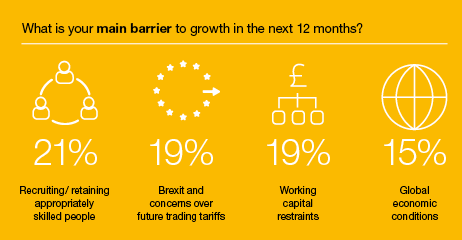
Among matters causing the most concern to manufacturing businesses are the potential impact of global trading issues, working capital restraints and recruiting and retaining skilled people.
It is also a clear view that a key factor to successful growth will be by seeking and exploiting global opportunities. Our survey shows the importance of appropriate and effective government incentives, but questions the effectiveness of those currently in place.
In conjunction with the Confederation of British Metalforming (CBM), we surveyed businesses across the UK manufacturing sector in winter 2019. Our findings cover a range of topics from the challenges faced when employing skilled workers, to the effectiveness of government schemes like the apprenticeship levy.
Business operation and growth
The survey showed a clear air of optimism regarding growth, with 59% of respondents expecting their turnover to increase in the next 12 months, whilst recruiting and retaining appropriately skilled staff was highlighted as the main barrier to growth by 21%.
Brexit and the UK economy
66% of respondents think Brexit will affect their business either moderately or significantly, with only 6% thinking it will have no affect at all. Key concerns raised about the impact on the sector relate to the talent pool and trade.
Key concerns that manufacturers face with the outcome of Brexit:
 Talent Pool
Talent Pool
85% of respondents see employing foreign workers as positive. Changes to UK immigration and border control and the potential introduction of a points based system will likely welcome skilled workers to the UK, increasing the talent pool for the manufacturing industry, but could limit access to unskilled labour. However, our survey indicates this may not be too much of an issue as only 40% of respondents feel they are affected by the National Minimum Wage.
 Trade
Trade
Increased tariff and trade complications, also currency dynamics could increase operating costs. Businesses want to ensure that they can carry on trading after Brexit and that any impact on their customers and supply chain is minimised. This means that traders will need to determine if there is any impact on the regulatory environment in which they operate and/or their business model and/or whether there is a need to setup operations in the EU if they have not already done so.
UK tax systems and government
While ‘Brexit and concerns over future trading tariffs’ were seen as a limit to growth for 19% of respondents, 15% were concerned about ‘Global economic conditions’ more generally.
Both scoredless than ‘recruiting/retaining appropriately skilled staff’, which concerned 21% of respondents.
Interestingly, however, the effectiveness of the apprenticeship levy system is severely criticised; seeing just 6% of respondents rating the scheme as ‘very effective’ and 60% rating it as ‘not so’ or ‘not at all’ effective.
 Difficulty in recruiting skilled people (81%) due primarily to lack of available skills, positivity shown for employing foreign nationals (85%) and an ambivalence towards the minimum wage (60% said that it does not affect their business), are clear indicator of pressures on availability of people.
Difficulty in recruiting skilled people (81%) due primarily to lack of available skills, positivity shown for employing foreign nationals (85%) and an ambivalence towards the minimum wage (60% said that it does not affect their business), are clear indicator of pressures on availability of people.
It is evident skills are seen as the largest restriction to achieving growth over the next year or so and there is a need for this to be better addressed by government.
Industry 4.0
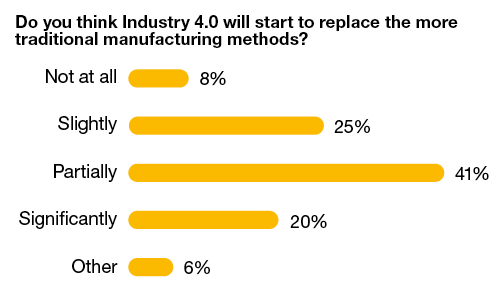 Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution, is a term that represents a number of automation, data exchange and manufacturing technologies. There are many technologies involved in this transformation, including artificial intelligence, 5G, big data, blockchain, cloud and edge computing, cyber security, immersive technology, the internet of things and robotics. We note that just 61% of respondents thought that Industry 4.0 methods will replace traditional ones, either significantly or partially, with an indication that generational issues and inertia will have an effect.
Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution, is a term that represents a number of automation, data exchange and manufacturing technologies. There are many technologies involved in this transformation, including artificial intelligence, 5G, big data, blockchain, cloud and edge computing, cyber security, immersive technology, the internet of things and robotics. We note that just 61% of respondents thought that Industry 4.0 methods will replace traditional ones, either significantly or partially, with an indication that generational issues and inertia will have an effect.
Exporting
International trade continues to dominate the news with trade wars and Brexit creating difficult trading conditions for UK importers and exporters. 80% of survey respondents did not consider the government’s incentives to be effective at promoting exporting.
 Funding
Funding
Our survey indicated that businesses in general have positive relationships with their bankers; a far cry from what might have been regarded as a nadir in these relationships, at the time of the ‘credit crunch’, with 76% of respondents having a good or very good relationship with their bank.
Sales and marketing
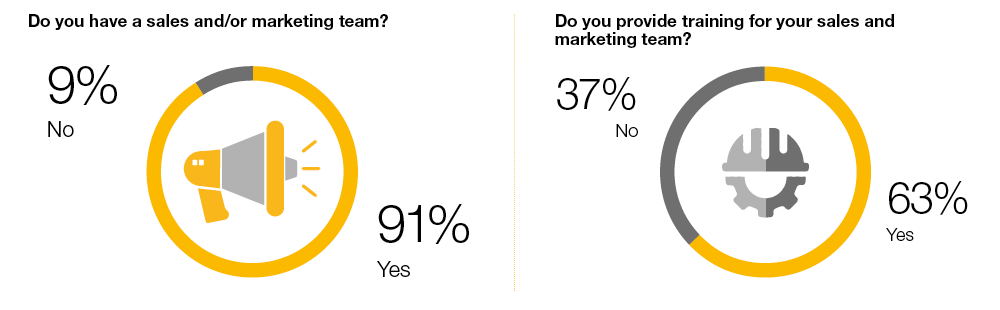
In a period where growth, according to our survey, is generally expected, and against a tough and dynamic European and Global commercial environment, it is essential that a manufacturer’s sales team functions effectively. Whilst 91% of respondents had a sales and/or marketing team, almost half considered their team to be less than 71% effective.
Download Manufacturing Outlook report
We hope that you find our report an interesting read and that it will help planning and decision making in the coming months, enabling your business to thrive.
Please complete the fields to receive the full download of our report.
Thank you for your interest in our report.
Download our Manufacturing Outlook report [pdf]
Crowe take data protection extremely seriously; we will never provide your details to any third party. View our full Privacy Policy.
Contact us